The Nervous System
Functions:
- Monitors changes in both internal and external environment
- Processes sensory inputs through integration
- Triggers a response to the sensory input through motor output
- Monitors changes in both internal and external environment
- Processes sensory inputs through integration
- Triggers a response to the sensory input through motor output
The Brain
http://whyfiles.org/siegfried/story27/
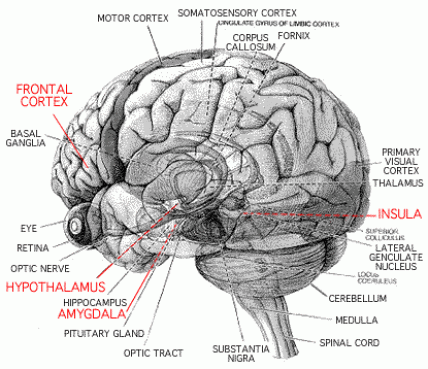
Medulla oblongata - Controls involuntary function, like heartbeat and breathing
Pons - Part of controlling movement, arousal and consciousness
Reticular Formation: Involved in the onset of sleep cycle
Thalamus - Part of the brain that regulates where certain signals have to go
Cerebrum - Controls thought, memory and senses, largest part of the brain
Amygdala - Triggers emotion
Hypothalamus - Responsible for responding to the body's needs, such as hunger, thirst, homeostasis and sleep
Corpus Callosum - Connects the two hemispheres of the brain
Hippocampus - Controls memory
Cerebellum - Coordinates conscious movement and balance
Spinal Cord - Controls simple reflexes, part of the central nervous system
Pituitary Gland - Controls endocrine system
Central Nervous System
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the control center for the nervous system, while the spinal cord connects neurons to the brain. Neurons carry information from sensory inputs to the brain, which allows for the five senses. Then, the brain delivers the motor output response.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral system is made up of the neurons connected to all parts of the body. It is divided into two parts: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system allows for conscious control over skeletal muscle, while the autonomic nervous system regulates the smooth muscle and glands found in inner organs that we cannot consciously control. The autonomic nervous system is then further divided into sympathetic ("fight or flight") and parasympathetic ("rest or digest").
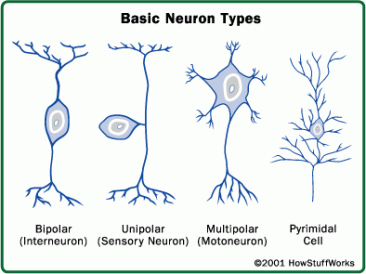
Types of Neurons
Sensory Neurons - Receptors for sensations such as touch, taste, sight, sound and smell
Motor Neurons - Transmit impulses to muscles and glands as a response
Interneurons - Found within the spinal cord and brain; stimulated by signals from sensory neurons or other interneurons
Sensory Neurons - Receptors for sensations such as touch, taste, sight, sound and smell
Motor Neurons - Transmit impulses to muscles and glands as a response
Interneurons - Found within the spinal cord and brain; stimulated by signals from sensory neurons or other interneurons