The Endocrine System
Functions:
- Regulates growth (pituitary)
- Regulates water balance (pituitary)
- Regulates reproduction (pituitary, ovaries/testes)
- Regulates metabolism (thyroid)
- Regulates calcium and gluclose levels (thyroid, parathyroid, pancrease)
- Regulates response to stress (adrenals)
- Regulates growth (pituitary)
- Regulates water balance (pituitary)
- Regulates reproduction (pituitary, ovaries/testes)
- Regulates metabolism (thyroid)
- Regulates calcium and gluclose levels (thyroid, parathyroid, pancrease)
- Regulates response to stress (adrenals)
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine glands lack ducts and release hormones into the bloodstream.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands release hormones into ducts. For example, tear glands create tears that travel through ducts leading directly to the eyes.
The endocrine system is comprised of glands throughout the body that secrete hormones. These hormones are chemical messengers that tell receptor cells what to do. The major glands are:
Hypothalamus
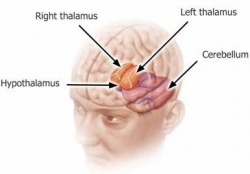
The hypothalamus is located in the lower central part of the brain. It releases hormones that control the pituitary by either stimulating or suppressing certain hormones produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary. One example is somatostatin, which stops the pituitary from releasing growth hormone. The hypothalamus can also make hormones stored in the posterior lobe of the pituitary. http://www.tiptopwebsite.com/websites/index2.php?username=aslenderme
Pituitary
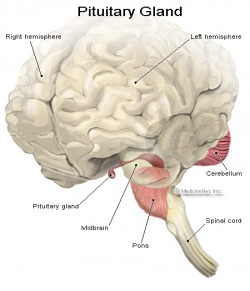
The pituitary is a very small gland located at the base of the brain under the hypothalamus. It is the master control center of the endocrine system. It is divided into the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The anterior lobe, regulated by the hypothalamus, produces growth hormone (GH - stimulates growth of bone and tissue), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH - stimulates the thyroid to produce its hormones), adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH - stimulates the adrenal gland to produce its hormones), luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (LH and FSH - control sexual function and production of sex steroids), and prolactin (stimulates milk production in females). The posterior lobe, which is not regulated by the hypothalamus, produces antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin - controls water loss in the kidneys) and oxytocin (contracts the uterus during childbirth). http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_endocrine_system/page11_em.htm
Thyroid
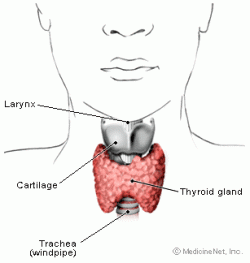
The thyroid is located in the lower front part of the throat. Its hormones are meant to regulate the body's metabolism through the hormone thyroxine. In addition, the thyroid helps with bone growth and brain development in children, as well as maintaining blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, muscle tone and reproductive function. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_endocrine_system/page11_em.htm
Parathyroid
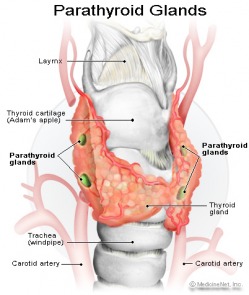
The parathyroid glands are actually two pairs of small glands located on each side of the thyroid gland. They release parathyroid hormone, which is important for regulating calcium levels in blood and bone tissue. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_endocrine_system/page11_em.htm
Adrenals
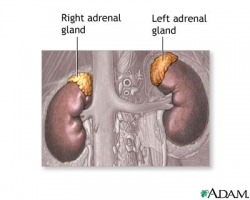
The adernals are two triangular glands located on top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex, the outer part, produces a classification of hormones known as corticosteroids. These help regulate the body's metabolism, the balance of salt and water in the body, the immune system, as well as sexual function. The adrenal medulla, the inner part, produces catecholamine hormones which help the body deal with physical and emotional stress through heart rate and blood pressure. The most well-known catecholamine hormone is adrenaline. Others include epipinephrine and norepinephrine. http://www.besthealth.com/besthealth/bodyguide/reftext/html/endo_sys_fin.html#adrenal
Pineal
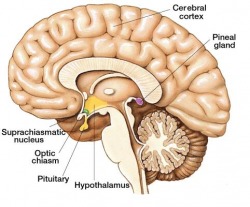
The pineal gland is in the middle of the brain. It produces hormones that control routine activity, such as melatonin, which regulates the body's wake-sleep cycle. http://history.wisc.edu/sommerville/351/351-19.htm
Testes
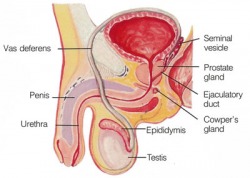
The reproductive gland in males is called the testes, located in the scrotum. It produces a group of hormones called androgens, the most important one being testosterone. These hormones create male characteristics, such as facial hair, sexual development and sperm production. https://www51.safesecureweb.com/malefertility/male_infertility_causes.html
Ovaries
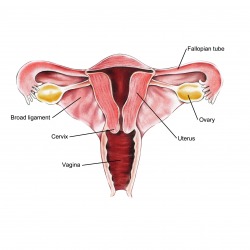
The reproductive gland in females is called the ovaries, located on both sides of the uterus. In addition to producing eggs, the ovaries produce two hormones called progesterone and estrogen. These hormones create female characteristics, such as breast growth and reproductive functions like menstruation and pregnancy. https://www51.safesecureweb.com/malefertility/male_infertility_causes.html
Pancreas
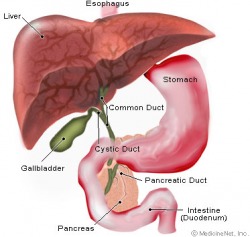
The pancreas is actually an organ located behind the stomach. The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine components. The exocrine part secretes digestive enzymes, while the endocrine part secretes insulin and glucagon. These two hormones regulate the level of glucose in the blood. Insulin causes glucose to be converted into glycogen, a stored form of energy. Glucagon accelerates the conversion of glycogen back into glucose. People with Diabetes either don't produce insulin (Type I) or are resistent to insulin (Type II), so they have too much glucose in their bodies.
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_endocrine_system/page11_em.htm
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/anatomy_of_the_endocrine_system/page11_em.htm
Thymus
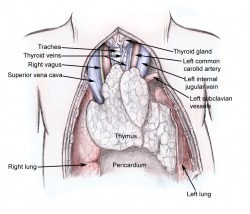
The thymus gland is located under the thyroid gland behind the sternum. It is most active during childhood, when it produces thymosins. These hormones produce T-lymphocytes, which are cells crucial to the immune system. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/427053-overview
