The Cardiovascular System
Functions:
- Delivers oxygen-rich blood, nutrients and hormones to the body's cells
- Carries oxygen-poor blood back to the heart
- Removes waste products
- Protects by transporting white blood cells to fight infection and forming blood clots to prevent blood loss
- Regulates body temperature, pH and water content of cells
- Delivers oxygen-rich blood, nutrients and hormones to the body's cells
- Carries oxygen-poor blood back to the heart
- Removes waste products
- Protects by transporting white blood cells to fight infection and forming blood clots to prevent blood loss
- Regulates body temperature, pH and water content of cells
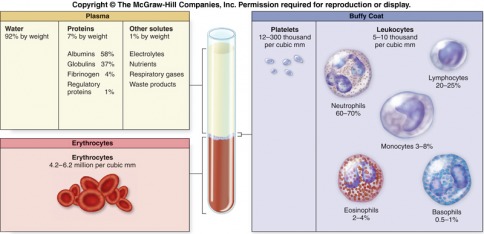
Blood is the liquid tissue that carries the body's nutrients and waste products to and from various parts of the body. Blood cells are formed from red bone marrow found inside bones. Blood mostly consists of:
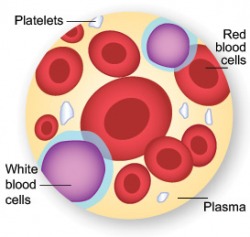
Plasma - Yellowish liquid, about 90% water. Also contains salts, glucose, proteins and the antibody that fights foreign blood types
Platelets/Thrombocytes - Help the blood to clot after a cut
Red Blood Cells/Erythrocytes - Carry oxygen throughout the body by attaching oxygen to a molecule called hemoglobin, contains the antigen protein that determines blood type
White Blood Cells/Leukocytes - Fight infection
Plasma - Yellowish liquid, about 90% water. Also contains salts, glucose, proteins and the antibody that fights foreign blood types
Platelets/Thrombocytes - Help the blood to clot after a cut
Red Blood Cells/Erythrocytes - Carry oxygen throughout the body by attaching oxygen to a molecule called hemoglobin, contains the antigen protein that determines blood type
White Blood Cells/Leukocytes - Fight infection
Vocabulary
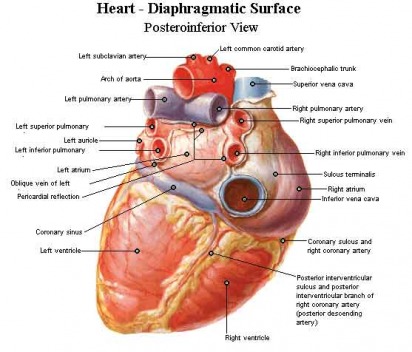
Adventitia - Tough outer covering of a blood vessel
Aortic Valve - Separates left ventricle from aorta
Aorta - Largest blood artery that sends oxygen-rich blood throughout the body
Arteries - Thickest, muscular blood vessels carrying blood away from the heart
Arterioles - Smaller arteries where blood reaches before the capillaries
Atria - Receive blood entering the heart
Atrioventricular Node - Receives electrical impulse after atria contract, then moves the impulse through the ventricles to make them contract
Atrioventricular Valve - Separates atria from ventricles
Blood Pressure - Force exerted by circulating blood on blood vessel walls; expressed in systolic pressure over diastolic pressure
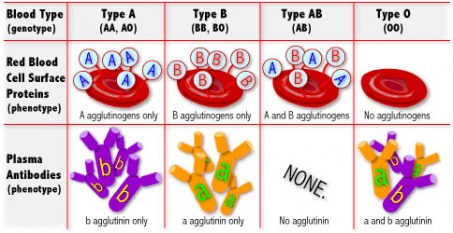
Blood Type - Classifies what kind of protein one's red blood cells carry: A, B, AB or O (the universal donor, and my blood type)
Capillaries - Tiny networks that connect veins and arteries; allows nutrients and oxygen to be delivered and waste products to be removed
Cardiac Cycle - One full heartbeat
Diastole - Second phase of cardiac cycle in which ventricles relax to fill with blood from the atria
Endothelium - Smooth inner lining of a blood vessel where blood passes over
Heart - Muscular, hollow organ at the center of the cardiovascular system, beats around 100,000 times a day
Inferior Vena Cava - One of the largest veins below the heart, receives oxygen-poor blood from the lower body and sends it to the right atrium
Interatrial Septum - Muscular wall separating right and left atrium
Interventricular Septum - Muscular wall separating right and left ventricle
Media - Muscular and elastic middle part of a blood vessel
Mitral Valve - Separates left atrium and left ventricle
Pulmonary Artery - Carries oxygen-poor blood from right ventricle to the lungs
Pulmonary Circulation - Blood flow from the heart to the lungs, path starts at the right ventricle and ends at the left atrium
Pulmonic Valve - Separates right ventricle from pulmonary artery
Pulmonary Vein - Carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left ventricle
Sinoatrial Node - Tissue area in right atrium wall that sends out electrical signals to make the heart contract
Superior Vena Cava - One of the largest veins above the heart, receives oxygen-poor blood from the head and arms and sends it to the right atrium
Systemic Circulation - Blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, path starts at the left ventricle and ends at the right atrium
Systole - First phase of cardiac cycle in which ventricles contract to send blood into circulation
Tricuspid Valve - Separates right atrium and right ventricle
Veins - Thinner, less muscular blood vessels carrying blood to the heart
Ventricles - Pump blood out of the heart
Venules - Smaller veins where blood reaches before the veins
Adventitia - Tough outer covering of a blood vessel
Aortic Valve - Separates left ventricle from aorta
Aorta - Largest blood artery that sends oxygen-rich blood throughout the body
Arteries - Thickest, muscular blood vessels carrying blood away from the heart
Arterioles - Smaller arteries where blood reaches before the capillaries
Atria - Receive blood entering the heart
Atrioventricular Node - Receives electrical impulse after atria contract, then moves the impulse through the ventricles to make them contract
Atrioventricular Valve - Separates atria from ventricles
Blood Pressure - Force exerted by circulating blood on blood vessel walls; expressed in systolic pressure over diastolic pressure
Blood Type - Classifies what kind of protein one's red blood cells carry: A, B, AB or O (the universal donor, and my blood type)
Capillaries - Tiny networks that connect veins and arteries; allows nutrients and oxygen to be delivered and waste products to be removed
Cardiac Cycle - One full heartbeat
Diastole - Second phase of cardiac cycle in which ventricles relax to fill with blood from the atria
Endothelium - Smooth inner lining of a blood vessel where blood passes over
Heart - Muscular, hollow organ at the center of the cardiovascular system, beats around 100,000 times a day
Inferior Vena Cava - One of the largest veins below the heart, receives oxygen-poor blood from the lower body and sends it to the right atrium
Interatrial Septum - Muscular wall separating right and left atrium
Interventricular Septum - Muscular wall separating right and left ventricle
Media - Muscular and elastic middle part of a blood vessel
Mitral Valve - Separates left atrium and left ventricle
Pulmonary Artery - Carries oxygen-poor blood from right ventricle to the lungs
Pulmonary Circulation - Blood flow from the heart to the lungs, path starts at the right ventricle and ends at the left atrium
Pulmonic Valve - Separates right ventricle from pulmonary artery
Pulmonary Vein - Carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left ventricle
Sinoatrial Node - Tissue area in right atrium wall that sends out electrical signals to make the heart contract
Superior Vena Cava - One of the largest veins above the heart, receives oxygen-poor blood from the head and arms and sends it to the right atrium
Systemic Circulation - Blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, path starts at the left ventricle and ends at the right atrium
Systole - First phase of cardiac cycle in which ventricles contract to send blood into circulation
Tricuspid Valve - Separates right atrium and right ventricle
Veins - Thinner, less muscular blood vessels carrying blood to the heart
Ventricles - Pump blood out of the heart
Venules - Smaller veins where blood reaches before the veins